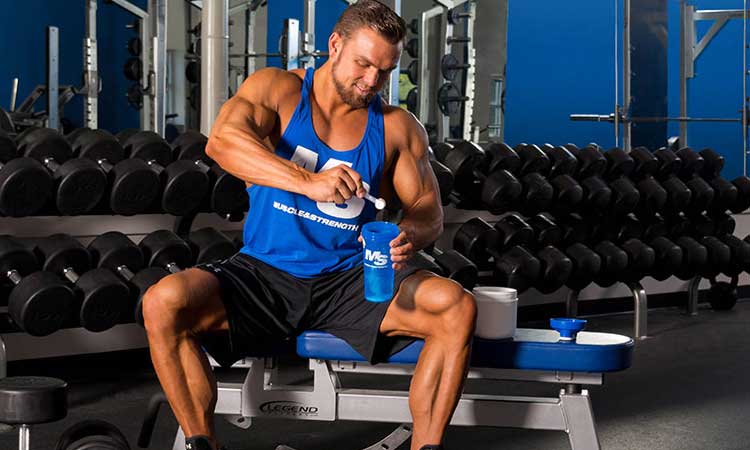
L-Glutamine is one of the essential amino acids in your body. It’s present in nearly every protein you consume and plays many crucial roles throughout the body. L-Glutamine is also essential to your immune system and gut barrier, protecting you from infections, toxins, and undigested food particles. It’s also an energy source for your intestines and aids with their growth and repair.
Increases Muscle Growth
Glutamine is essential for protein synthesis, so it plays a vital role in muscle growth and repair. In addition, it supports your body’s ability to secrete human growth hormone, which is essential for maintaining muscle mass and promoting growth in new muscles.
During physical stress, such as intense exercise and surgery, glutamine levels in the body are depleted quickly. When this happens, supplementation with L-glutamine helps maintain glutamine levels.
This is particularly important for athletes who are undergoing high-intensity training. Taking a supplement with glutamine during exercise can reduce your risk of overtraining syndrome, characterized by diminished strength and performance.
In addition to strengthening your muscles, glutamine helps protect your immune system and digestive health. It is a key fuel for your gut cells and helps prevent bacteria from entering the small intestine. In addition, you should also know what are the benefits of l-glutamine. It has anti-catabolic properties, which keep your muscles from breaking down during training. This makes it a must-have for any athlete or fitness enthusiast looking to build lean muscle and improve their strength.
Increases Muscle Repair
Glutamine is the body’s major nitrogen-carrying amino acid. It’s found in various foods, including meat, fish, eggs and dairy products.
L-glutamine is essential for building muscle mass and repairing damaged muscles. It also plays a vital role in restoring the balance of nitrogen.
As a result, athletes need to ensure they get enough glutamine in their diet. This is especially true for endurance athletes.
Long-distance runners benefit from glutamine by increasing their T-helper cells and reducing the fatigue associated with overtraining syndrome.
In addition, L-glutamine helps prevent lactic acid buildup. This results in a more robust and faster recovery period for athletes after an intense workout or race.
It’s also a potent ammonia scavenger and improves sodium uptake in skeletal muscles, which reduces fatigue. In addition to these benefits, glutamine promotes intestinal health and supports healthy bowel movements by balancing mucus production. This is especially helpful for people with leaky guts. A leaky gut can lead to several conditions, including thyroid problems, arthritis and skin issues like psoriasis.
Increases Muscle Strength
Glutamine is one of the essential amino acids in the human body. It is the most abundant of the 20 naturally occurring amino acids in protein foods.
Despite its abundant availability in a balanced diet, glutamine levels decrease with exercise. This is because movement causes the release of stress hormones that break down muscle tissue.
Therefore, it is essential to replenish glutamine levels with supplements after exercise. By increasing glutamine levels, muscles are better able to repair and grow.
L-glutamine supplementation also enhances performance during high-intensity workouts. It regulates muscle glucose uptake, a key energy source during exercise.
If you are an endurance athlete or a bodybuilder who works out several times per week, taking L-glutamine before and after workouts can help reduce the stress your body is under during activities and increase recovery time.
Athletes who supplement with L-glutamine can see improved results from their training regimens and prevent injuries. However, checking with your doctor before starting any supplement program is best, as some medications can interact with L-glutamine.
Increases Muscle Power
Glutamine is an amino acid that promotes muscle recovery and reduces the soreness associated with exercise. It also helps maintain a positive nitrogen balance, critical for muscle growth and repair.
The human body naturally produces glutamine but can become depleted under heavy stress, such as long workouts or high-intensity training. Supplementing with L-glutamine can help preserve this amino acid in the body.
This amino acid can be found in various foods, including beans, nuts, and seeds. It can also be supplemented in powder form.
As an amino acid, glutamine helps the body synthesize proteins, hormones and more. Moreover, it can support the immune system and assist with fat loss.
Another essential function of glutamine is regulating glucose and glycogen in the body. When the liver cannot convert glycogen into glucose, it sends the signal to release L-glutamine.
The kidneys also use it to keep the body’s acid-base balance in check. It cleaves excess ammonia from the bloodstream and converts it into other amino acids, sugars, or urea.
Increases Muscle Mass
Glutamine helps you recover faster from your workout by regulating the amount of glucose and glycogen your body releases. It also supports the immune system and facilitates muscle protein synthesis.
In addition, glutamine can draw salt and water into your muscles to help them expand and swell as they repair and grow after a workout. This process promotes new muscle cells’ growth, increasing your muscle mass and strength.
It helps you build lean muscle while reducing the amount of fat mass. A study found that collegiate athletes who took four grams of glutamine daily for eight weeks increased their lean-body mass more than those taking creatine alone.
However, it’s important to note that this study was small, requiring higher doses for more significant results. Research suggests that 5 to 10 grams is sufficient for most people, and 15 to 30 grams is recommended for those with inflammatory bowel diseases or under significant stress.